Dendritic Cells
Dendritic Cells
What are dendritic cells?
Dendritic cells are a type of immune cell known since the 1970s (Steinman et al.). They are classified in the category of APCs (Antigen Presenting Cells), ie cells that present the various antigens in T- and B-lymphocytes, so that they can be properly differentiated, and the immune response to the disease can occur. Dendritic cells are considered to be the pacemakers of the immune system. In fact, it is the key cells in this immune system. They are critical for triggering the immune response of T-lymphocytes, which eventually produce cellular immunity.
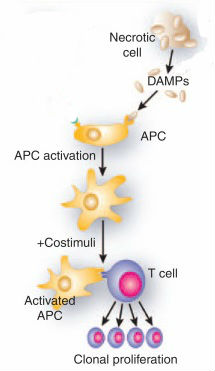
Dendritic cells are produced by precursor immune cells. Antecedent progenitors phagocytose antigens they encounter, process them, and reorganize antigenic proteins into peptides, which are then externalized to the cell surface, where they bind to proteins in the major histocompatibility system. This is how mature dendritic cells are produced.
Dendritic cells carry protein molecules that belong to the major tissue compatibility system. These molecules generally attach various antigens to the surface of the dendritic cell. Because, in the case of malignancies, the rate of apoptosis is very limited, not enough apoptomes and DAMPs (Damage Associated Molecular Patterns) are usually produced, so the dendritic cells do not provide antigens derived from the tumor. This is one of the reasons why the immune system does not deal effectively with cancers. However, under the influence of various therapeutic stimuli, such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, oncothermia, etc., cancer cells are led to apoptosis, apoptosis and DAMPs are produced, they bind to dendritic cells and present them in T-lymphocytes.
- After all, how do cancer cells get killed?
- What is the treatment with dendritic cells (DK)?
- Is there a relationship between dendritic cells and oncothermia?
Why in Personalized Oncology?
With personalization in oncology we are able to revive the patient's hope.
While we do not despise the therapeutic means of conventional oncology, on the contrary, we enrich the treatment....
More

